-
Table of Contents
Erythropoietin: Mechanism of Action and Impact on Physical Endurance
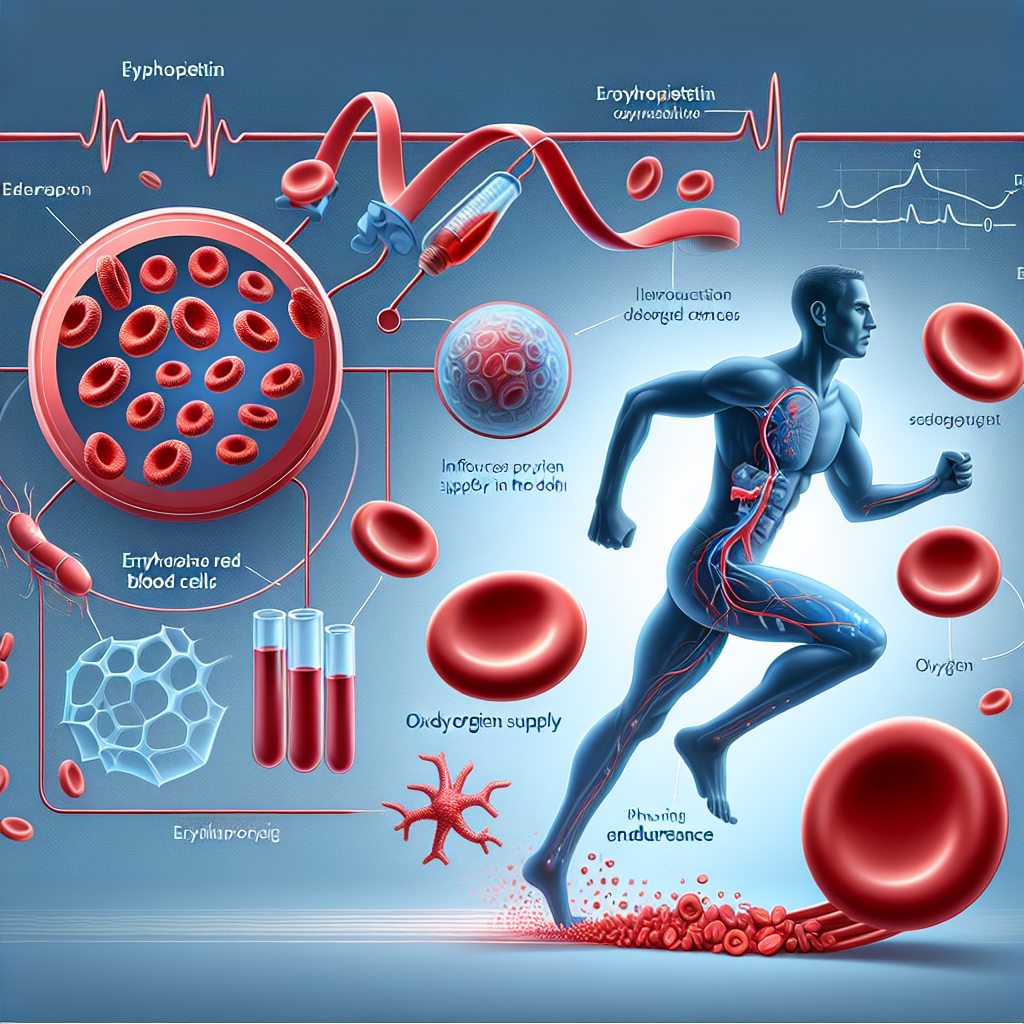
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone that plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells (RBCs) in the body. It is primarily produced by the kidneys and is responsible for regulating the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity. In recent years, EPO has gained significant attention in the world of sports as a performance-enhancing drug. This article will delve into the mechanism of action of EPO and its impact on physical endurance, backed by scientific evidence and expert opinions.
Mechanism of Action
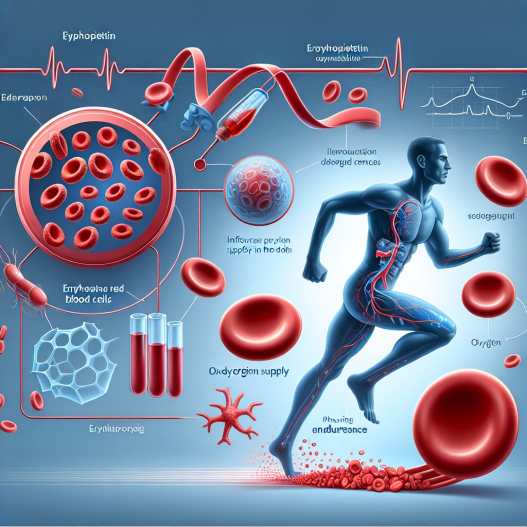
The primary function of EPO is to stimulate the production of RBCs in the bone marrow. It does so by binding to specific receptors on the surface of erythroid progenitor cells, which are responsible for the production of RBCs. This binding triggers a cascade of events that ultimately leads to the production of more RBCs.
EPO also plays a crucial role in the maturation of RBCs. It promotes the differentiation of erythroid progenitor cells into mature RBCs, which are then released into the bloodstream. This process is essential for maintaining the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity and ensuring adequate oxygen supply to the tissues.
In addition to its role in RBC production, EPO also has anti-apoptotic effects. It protects cells from programmed cell death, which is crucial for the survival and maintenance of RBCs in the body. This anti-apoptotic effect is particularly beneficial for athletes who engage in high-intensity and endurance activities, as it helps prevent the premature death of RBCs due to physical stress.
Impact on Physical Endurance
The increase in RBC production and oxygen-carrying capacity induced by EPO has a significant impact on physical endurance. Studies have shown that EPO administration can improve an athlete’s aerobic capacity, allowing them to perform at a higher intensity for a longer duration (Lundby et al. 2012). This is because the increased RBC count allows for more efficient oxygen delivery to the muscles, delaying the onset of fatigue.
EPO has also been shown to improve an athlete’s recovery time. By increasing the oxygen-carrying capacity, EPO can help replenish the oxygen debt incurred during intense physical activity, allowing for a quicker recovery and reduced muscle soreness (Birkeland et al. 2000). This is particularly beneficial for athletes who engage in multiple events or competitions in a short period.
Furthermore, EPO has been found to improve an athlete’s overall performance. In a study conducted on cyclists, it was found that EPO administration resulted in a 6% increase in performance during a time trial (Ekblom et al. 1994). This improvement in performance can be attributed to the increased oxygen delivery to the muscles, allowing for a higher power output and faster speeds.
Real-World Examples
The use of EPO in sports has been a controversial topic, with several high-profile cases of athletes being caught using the drug to enhance their performance. One such example is the case of cyclist Lance Armstrong, who admitted to using EPO during his seven Tour de France victories (BBC Sport 2013). This highlights the significant impact of EPO on physical endurance and its potential for abuse in the world of sports.
Another real-world example is the case of cross-country skier Johann Mühlegg, who was stripped of his Olympic gold medals in 2002 after testing positive for EPO (BBC Sport 2002). This case further emphasizes the need for strict regulations and testing in sports to prevent the use of performance-enhancing drugs like EPO.
Expert Opinion
According to Dr. Michael Joyner, a sports physiologist and expert in performance-enhancing drugs, EPO can provide a significant advantage to athletes in endurance sports (Joyner 2013). He also notes that the use of EPO in sports is not a new phenomenon and has been prevalent since the 1990s. However, he stresses the importance of ethical considerations and the potential health risks associated with EPO use.
Conclusion
EPO is a hormone with a crucial role in the production of RBCs and the regulation of the body’s oxygen-carrying capacity. Its use in sports has been a topic of controversy, with several high-profile cases of athletes being caught using the drug. However, scientific evidence and expert opinions suggest that EPO can significantly impact an athlete’s physical endurance, improving their performance and recovery time. Strict regulations and testing are necessary to prevent the abuse of EPO in sports and ensure a level playing field for all athletes.
References
BBC Sport. (2013). Lance Armstrong admits to doping to win Tour de France titles. Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/sport/cycling/21036489
BBC Sport. (2002). Muehlegg stripped of gold medals. Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/sport/winter-olympics/18002644
Birkeland, K. I., Stray-Gundersen, J., Hemmersbach, P., Hallen, J., & Haug, E. (2000). Effect of rhEPO administration on serum levels of sTfR and cycling performance. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, 32(7), 1238-1243.
Ekblom, B., Berglund, B., & Birkeland, K. I. (1994). Effect of erythropoietin administration on maximal aerobic power. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine and Science in Sports, 4(2), 88-93.
Joyner, M. (2013). Erythropoietin: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Retrieved from https://www.sportsscientists.com/2013/01/erythropoietin-the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly/
Lundby, C., Robach, P., & Boushel, R. (2012). Erythropoietin: Endogenous production, performance-enhancing effects, and detection methods. Journal of Applied Physiology, 113(8), 1268-1276.